
Demystifying Cholesterol: Good vs. Bad and What You Need to Know
Demystifying Cholesterol: Good vs. Bad and What You Need to Know
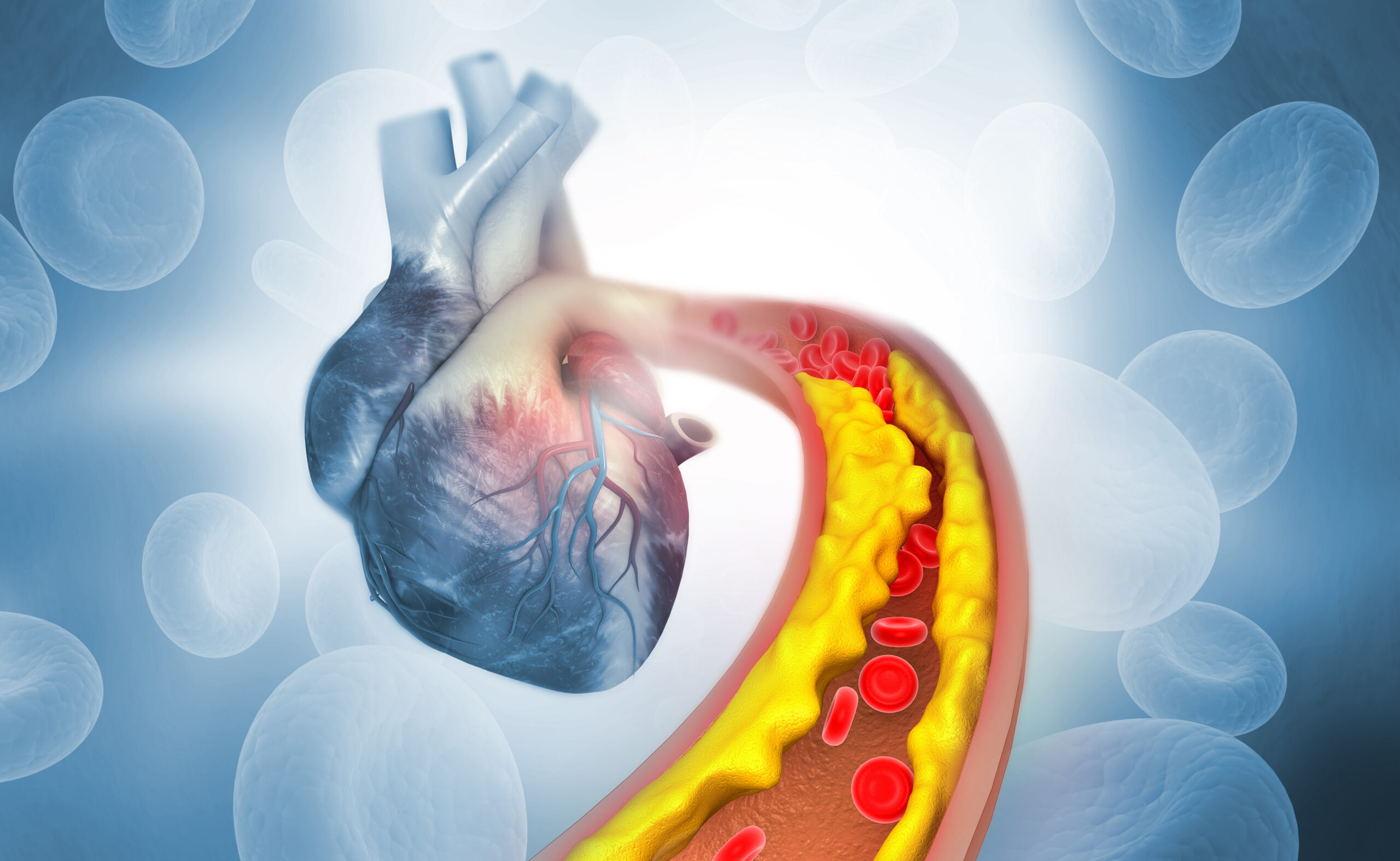
Cholesterol often gets a bad rap, but it’s actually an essential substance for our bodies. The key is understanding the difference between good and bad cholesterol and how they affect heart health. In this blog post, we’ll clarify the differences between LDL (bad) and HDL (good) cholesterol, their roles in the body, and provide tips on managing cholesterol levels effectively.
Understanding Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a fatty substance found in every cell of your body. It’s necessary for producing hormones, vitamin D, and substances that help you digest foods. Your body makes all the cholesterol it needs, but it’s also found in some foods. To gain a deeper understanding of cholesterol, visit American Heart Association: What is Cholesterol?1.
The Types of Cholesterol: LDL vs. HDL
LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) – The “Bad” Cholesterol
LDL cholesterol is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol because high levels can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries. This buildup narrows the arteries and increases the risk of heart disease, heart attack, and stroke.
High LDL levels are commonly linked to a diet high in saturated and trans fats. For more on LDL cholesterol, check out Mayo Clinic: LDL Cholesterol2.
HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) – The “Good” Cholesterol
HDL cholesterol is known as “good” cholesterol because it helps remove other forms of cholesterol from your bloodstream. Higher levels of HDL are associated with a lower risk of heart disease.
HDL carries cholesterol from other parts of your body back to your liver, which then removes the cholesterol from your body. Learn more about HDL cholesterol at MedlinePlus: HDL Cholesterol3.
Effects on Heart Health
The balance between LDL and HDL cholesterol is crucial for heart health. When LDL levels are too high or HDL levels are too low, it can lead to atherosclerosis, where arteries become clogged and hardened. This condition significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular events.
Managing Cholesterol Levels
1. Eat Heart-Healthy Foods
Adopting a heart-healthy diet can help manage cholesterol levels effectively. Here are some dietary tips:
- Limit Saturated and Trans Fats: Reduce consumption of red meat, full-fat dairy products, and processed foods.
- Increase Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Foods like salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds are rich in omega-3s, which can improve heart health.
- Eat More Soluble Fiber: Foods such as oats, beans, lentils, and fruits can help reduce the absorption of cholesterol into your bloodstream.
- Choose Healthy Fats: Use olive oil, avocado, and nuts instead of butter or lard.
For a detailed guide on heart-healthy eating, visit Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health: The Nutrition Source4.
2. Exercise Regularly
Physical activity can help raise HDL cholesterol while lowering LDL cholesterol. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise each week, along with muscle-strengthening activities twice a week. Guidelines for physical activity can be found at CDC: How Much Physical Activity Do Adults Need?5.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Being overweight or obese can increase bad cholesterol and decrease good cholesterol. By losing even a small percentage of your body weight, you can improve your cholesterol levels. For weight management tips, refer to NHLBI: Aim for a Healthy Weight6.
4. Quit Smoking
Smoking lowers HDL cholesterol and damages the inner lining of arteries, making them more susceptible to cholesterol buildup. Quitting smoking can improve your HDL levels and overall cardiovascular health. Resources for quitting smoking are available at Smokefree.gov7.
5. Consider Medication
In some cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be enough to manage cholesterol levels. Your doctor may prescribe medication to help lower your LDL levels if necessary. For more information on cholesterol-lowering medications, visit American Heart Association: Medications for Cholesterol8.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between LDL and HDL cholesterol and their effects on heart health is vital for managing cholesterol levels effectively. By making heart-healthy dietary choices, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and considering medication if needed, you can keep your cholesterol levels in check and reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease.
To schedule and appointment with top our cardiologists at Sam Houston Heart and Vascular visit
www.samhoustonheart.com or call 832-241-2001
Footnotes
- American Heart Association: What is Cholesterol? ↩
- Mayo Clinic: LDL Cholesterol ↩
- MedlinePlus: HDL Cholesterol ↩
- Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health: The Nutrition Source ↩
- CDC: How Much Physical Activity Do Adults Need? ↩
- NHLBI: Aim for a Healthy Weight ↩
- Smokefree.gov ↩
- American Heart Association: Medications for Cholesterol ↩

